Interesting and somewhat upbeat discussion with IBM's Arvind Krishna on the Future of AI and Quantum Computing.
Quantum Mechanics
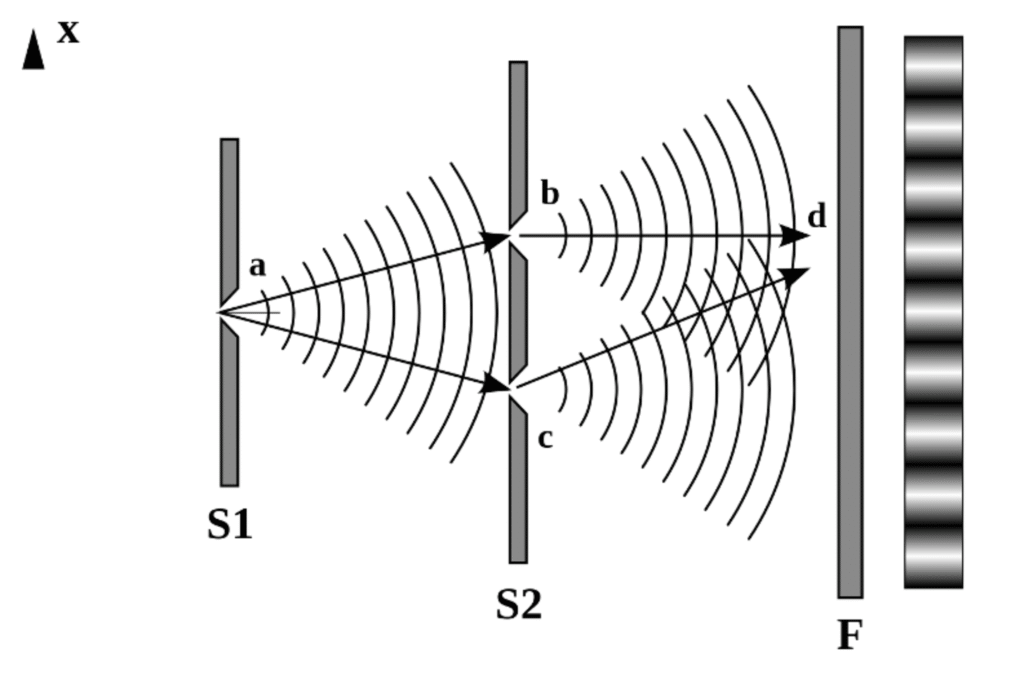
Quantum mechanics describes matter and energy behavior at the smallest imaginable scales, challenging our intuitive understanding of reality. Richard Feynman famously quipped that nobody truly understands quantum mechanics, yet its predictions have been consistently validated and its applications underpin modern technologies from transistors to lasers.At the quantum level, particles exhibit bizarre behaviors that defy classical physics. They can exist as both waves and particles simultaneously, demonstrating wave-particle duality through experiments like the double-slit test.
Quantum superposition allows particles to exist in multiple states at once until measured, while quantum entanglement enables instantaneous connections between particles regardless of distance – what Einstein called “spooky action at a distance.”Practical applications of quantum mechanics extend far beyond theoretical physics.
Quantum principles already enable everyday technologies like semiconductor electronics and laser systems. More revolutionary applications are emerging through quantum computing, where companies like IBM, Google, Microsoft, Intel, and others compete to develop machines that harness quantum effects for unprecedented computational power. These quantum computers could transform fields from cryptography to drug discovery, though significant technical challenges remain.
Current quantum computing capabilities range widely among competitors. IBM has achieved over 400 qubits and offers cloud-based quantum computing services. Google demonstrated quantum supremacy with its Sycamore processor performing calculations far faster than classical supercomputers. D-Wave systems utilize quantum annealing with over 5000 qubits for specialized applications. Major tech companies continue investing heavily in quantum research and development.
Dive deep into what quantum chips are, how they work, and their transformative potential in various fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and artificial intelligence.
In a February 25 article Josh Peck provided a robut perspective on recent advances in Quantum Computing. https://joshpeck.substack.com/p/quantum-computing-is-officially-here?utm_source=post-email-title&publication_id=3542131 Quantum computing represents a revolutionary advancement beyond traditional computing, evolving from the electronic calculators of the 1960s. Unlike conventional computers that use binary bits (1s and 0s), quantum computers leverage qubits which can exist in multiple states simultaneously through “superposition” and can be connected through “quantum entanglement.” These technological advancements connect to biblical prophecy regarding the acceleration of knowledge in end times.Recent breakthroughs in quantum computing include University of Oxford’s achievement in wireless quantum algorithm transmission between processors and advancements in quantum computer scaling methods. Microsoft’s Majorana 1 processor uses Majorana particles to create more stable qubits, while Google’s Willow chip implements error correction capabilities. Both technologies demonstrate extraordinary computational power—Google claims Willow can solve certain problems in minutes that would take conventional supercomputers septillions of years to complete.
